Toll Free Helpline (India): 1800 1234 070
Rest of World: +91-9810852116
Free Publication Certificate
Vol. 3, Issue 11 (2015)
Optimization of malachite green decolourization by Pseudomonas aeruginosa MTCC 424
Author(s):
R. Santhi, M.S. Nalina Sundari
R. Santhi, M.S. Nalina Sundari
Abstract:
The triphenylmethane dye, malachite green used widely in various industrial processes possesses severe environmental concern, causing major health problems to human beings. In the present study, decolourization of malachite green using Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MTCC 424) was investigated by screening and optimizing various parameters to determine the optimal conditions required for maximum decolourization. Based on the studies, Pseudomonas aeruginosa showed maximum decolourization upon incubation for 18 hrs at 37 °C at pH 7. The decolourization was also enhanced by amending glucose and peptone as carbon and nitrogen sources in the culture medium. The present investigation reveals that the strain, Pseudomonas aeruginosa MTCC 424 showed great potential in the decolourization of malachite green dye up to 86 % in the aqueous environment at optimal conditions.
The triphenylmethane dye, malachite green used widely in various industrial processes possesses severe environmental concern, causing major health problems to human beings. In the present study, decolourization of malachite green using Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MTCC 424) was investigated by screening and optimizing various parameters to determine the optimal conditions required for maximum decolourization. Based on the studies, Pseudomonas aeruginosa showed maximum decolourization upon incubation for 18 hrs at 37 °C at pH 7. The decolourization was also enhanced by amending glucose and peptone as carbon and nitrogen sources in the culture medium. The present investigation reveals that the strain, Pseudomonas aeruginosa MTCC 424 showed great potential in the decolourization of malachite green dye up to 86 % in the aqueous environment at optimal conditions.
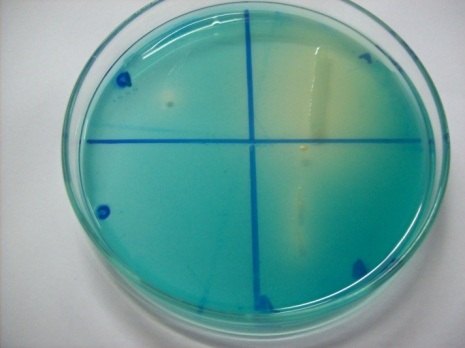
Fig.: Plate assay for malachite green decolourization
Pages: 11-15 | 2056 Views 177 Downloads

How to cite this article:
R. Santhi, M.S. Nalina Sundari. Optimization of malachite green decolourization by Pseudomonas aeruginosa MTCC 424. Pharma Innovation 2015;3(11):11-15.






