Toll Free Helpline (India): 1800 1234 070
Rest of World: +91-9810852116
Free Publication Certificate
Vol. 3, Issue 6 (2014)
Kinetic and docking studies reveal aldose reductase inhibition potential of edible lichen Parmotrema tinctorum
Author(s):
Jomon Sebastian, Prathapan A, Priya Sulochana, Raghu KG
Jomon Sebastian, Prathapan A, Priya Sulochana, Raghu KG
Abstract:
The present study investigated the aldose reductase inhibition potential of edible lichen Parmotrema tinctorum (Nyle.) Hale. The kinetics of aldose reductase inhibition by ethyl acetate extract (PTEAE) and ethanol extract (PTEE) of P. tinctorum has shown that PTEAE is competitive inhibitor while PTEE is a mixed inhibitor. Molecular docking of major constituents in P. tinctorum against aldose reductase revealed that usnic acid possesses the highest docking potential with a binding energy of -8.9 kcal/mol. The inhibition constant (Ki), was found to be 300.42 nM for usnic acid which is closer to the inhibition constant of the standard zopolrestat of 26.0 nM. The images of aldose reductase docked with atranorin, salazinic acid and usnic acid show that they have an interaction with Leu301 which is a nonpolar residue in the active site pocket of aldose reductase and conserved in both human and rat. This indicates that atranorin, salazinic acid and usnic acid bind to aldose reductase in a competitive fashion. Both kinetic and docking studies unraveled the aldose reductase inhibition potential ofP. tinctorum. Further studies on this will definitely lead to the development of a potential drug from P. tinctorum against diabetic cataract and retinopathy in future.
The present study investigated the aldose reductase inhibition potential of edible lichen Parmotrema tinctorum (Nyle.) Hale. The kinetics of aldose reductase inhibition by ethyl acetate extract (PTEAE) and ethanol extract (PTEE) of P. tinctorum has shown that PTEAE is competitive inhibitor while PTEE is a mixed inhibitor. Molecular docking of major constituents in P. tinctorum against aldose reductase revealed that usnic acid possesses the highest docking potential with a binding energy of -8.9 kcal/mol. The inhibition constant (Ki), was found to be 300.42 nM for usnic acid which is closer to the inhibition constant of the standard zopolrestat of 26.0 nM. The images of aldose reductase docked with atranorin, salazinic acid and usnic acid show that they have an interaction with Leu301 which is a nonpolar residue in the active site pocket of aldose reductase and conserved in both human and rat. This indicates that atranorin, salazinic acid and usnic acid bind to aldose reductase in a competitive fashion. Both kinetic and docking studies unraveled the aldose reductase inhibition potential ofP. tinctorum. Further studies on this will definitely lead to the development of a potential drug from P. tinctorum against diabetic cataract and retinopathy in future.
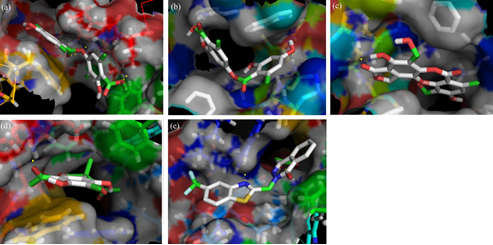
Fig.: Stereoview of aldose reductase docked with (a) atranorin, (b) lecanoric acid (c) salazinic acid, (d) usnic acid and (e) zopolrestat
Pages: 04-08 | 3628 Views 185 Downloads

How to cite this article:
Jomon Sebastian, Prathapan A, Priya Sulochana, Raghu KG. Kinetic and docking studies reveal aldose reductase inhibition potential of edible lichen Parmotrema tinctorum. Pharma Innovation 2014;3(6):04-08.






