Toll Free Helpline (India): 1800 1234 070
Rest of World: +91-9810852116
Free Publication Certificate
Vol. 3, Issue 4 (2014)
Humoral markers of endothelial dysfunction and systemic inflammatory response in patients with acute myocardial infarction depending on genes polymorphism of ACE (I/D) and eNOS (894G>T)
Author(s):
Larysa Sydorchuk, Yulia Ursuliak, Andriy Sydorchuk, Iryna Makoviychuk, Volodymir Trutiak, Igor Biryuk
Larysa Sydorchuk, Yulia Ursuliak, Andriy Sydorchuk, Iryna Makoviychuk, Volodymir Trutiak, Igor Biryuk
Abstract:
The dynamics of endothelial dysfunction (ED) humoral factors: a soluble form of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (sVCAM-1), total NO metabolites and systemic inflammatory response Â- C-reactive protein (CRP) in patients with acute myocardial infarction (MI) under the influence of treatment and depending on genes polymorphism – angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE, I/D) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS, T894G) were evaluated. The presence of DD-genotype of ACE gene is associated with a significantly greater decrease of sVCAM-1 and CRP levels under the influence of treatment (better with thrombolytic therapy (TLT), p<0.05); in T- allele carriers of eNOS gene the level sVCAM-1 under TLT decreased by 30.7-31.2%. Content of NO metabolites decreased more in D-allele carriers of ACE gene as well as after combined treatment with TLT (39.1% and 35.2%) and did not depend on the allele state of eNOS gene.
The dynamics of endothelial dysfunction (ED) humoral factors: a soluble form of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (sVCAM-1), total NO metabolites and systemic inflammatory response Â- C-reactive protein (CRP) in patients with acute myocardial infarction (MI) under the influence of treatment and depending on genes polymorphism – angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE, I/D) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS, T894G) were evaluated. The presence of DD-genotype of ACE gene is associated with a significantly greater decrease of sVCAM-1 and CRP levels under the influence of treatment (better with thrombolytic therapy (TLT), p<0.05); in T- allele carriers of eNOS gene the level sVCAM-1 under TLT decreased by 30.7-31.2%. Content of NO metabolites decreased more in D-allele carriers of ACE gene as well as after combined treatment with TLT (39.1% and 35.2%) and did not depend on the allele state of eNOS gene.
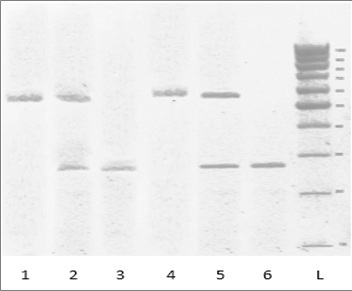
Fig.: Electrophoregramm of human DNA PCR products amplification of ACE I/D gene polymorphism. Note: L – DNA Ladder "GeneRulerÔ 100 bp" (1000-100 bp); lines 1, 4 – homozygous II genotype; lines 2, 5 – heterozygous ID variant; lines 3, 6 – homozygous DD variant.
Pages: 01-10 | 1702 Views 87 Downloads

How to cite this article:
Larysa Sydorchuk, Yulia Ursuliak, Andriy Sydorchuk, Iryna Makoviychuk, Volodymir Trutiak, Igor Biryuk. Humoral markers of endothelial dysfunction and systemic inflammatory response in patients with acute myocardial infarction depending on genes polymorphism of ACE (I/D) and eNOS (894G>T). Pharma Innovation 2014;3(4):01-10.







