Toll Free Helpline (India): 1800 1234 070
Rest of World: +91-9810852116
Free Publication Certificate
Vol. 2, Issue 11 (2014)
Diabetes Mellitus – An overview
Author(s):
S Ramachandran, A V Bhanu keerthi, M.D. Dhana Raju
S Ramachandran, A V Bhanu keerthi, M.D. Dhana Raju
Abstract:
Diabetes mellitus, or simply diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced. This high blood sugar produces the classical symptoms of polyuria, (frequent urination), polydypsia (increased thirst), and polyphagia (increased hunger).
There are three main types of diabetes mellitus (DM).
Diabetes mellitus, or simply diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced. This high blood sugar produces the classical symptoms of polyuria, (frequent urination), polydypsia (increased thirst), and polyphagia (increased hunger).
There are three main types of diabetes mellitus (DM).
- Type 1 DM results from the body's failure to produce insulin, and currently requires the person to inject insulin or wear an insulin pump. This form was previously referred to as "insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus" (IDDM) or "juvenile diabetes".
- Type 2 DM results from insulin resistance, a condition in which cells fail to use insulin properly, sometimes combined with an absolute insulin deficiency. This form was previously referred to as non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) or "adult-onset diabetes".
- The third main form, gestational diabetes, occurs when pregnant women without a previous diagnosis of diabetes develop a high blood glucose level. It may precede development of type 2 DM.
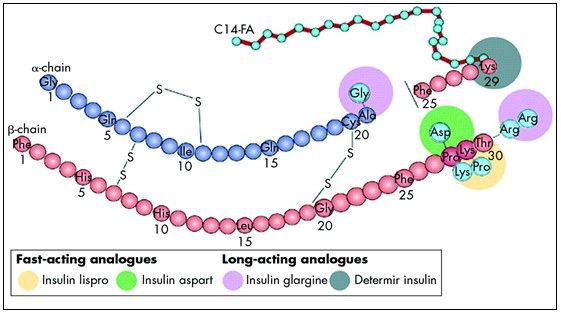
Fig.: Structure of insulin and the site of actions of insulin analogues
Pages: 27-37 | 1797 Views 113 Downloads

How to cite this article:
S Ramachandran, A V Bhanu keerthi, M.D. Dhana Raju. Diabetes Mellitus – An overview. Pharma Innovation 2014;2(11):27-37.







